Over the last year or so, we’ve seen a string of articles and papers about the small but sudden growth of the internet throughout the Pacific region. Ranging in tone between cautious optimism and untempered –and often uncritical– enthusiasm, few capture the essence of the struggle that Pacific island states face even keeping pace with the rate of change in the world of telecommunications and the internet.
 The internet is putting down tenuous roots in the Pacific – but do we really understand how to foster its growth?
The internet is putting down tenuous roots in the Pacific – but do we really understand how to foster its growth?
Over the last year or so, we’ve seen a string of articles and papers about the small but sudden growth of the internet throughout the Pacific region. Ranging in tone between cautious optimism and untempered –and often uncritical– enthusiasm, few capture the essence of the struggle that Pacific island states face even keeping pace with the rate of change in the world of telecommunications and the internet.
When I first arrived in Vanuatu the better part of a decade ago, the entire country was sharing only slightly more bandwidth than I’d had at my personal disposal back in Canada. To add insult to injury, the cost was roughly ten times greater even for the paltry amounts on sale. Getting access to what would be considered even a nominal connection in the developed world involved expenditures equivalent to thousands of dollars a month.
Now, following years of consistent and determined effort, Vanuatu has widely available commercial internet in its urban areas. But prices remain high. As this piece is being written, the cost of a 2 megabit connection (the lowest tier of what is considered broadband in many developed nations) starts at about AUD800 per month, and rises quickly once usage fees are factored in.
In spite of this, internet service providers have found inventive ways to get people started, offering small (cynics might say paltry) connection speeds and bandwidth limits. Comparisons aside, such packages are at least sufficient to move the uptake indicator from effectively zero to… something slightly more than zero.
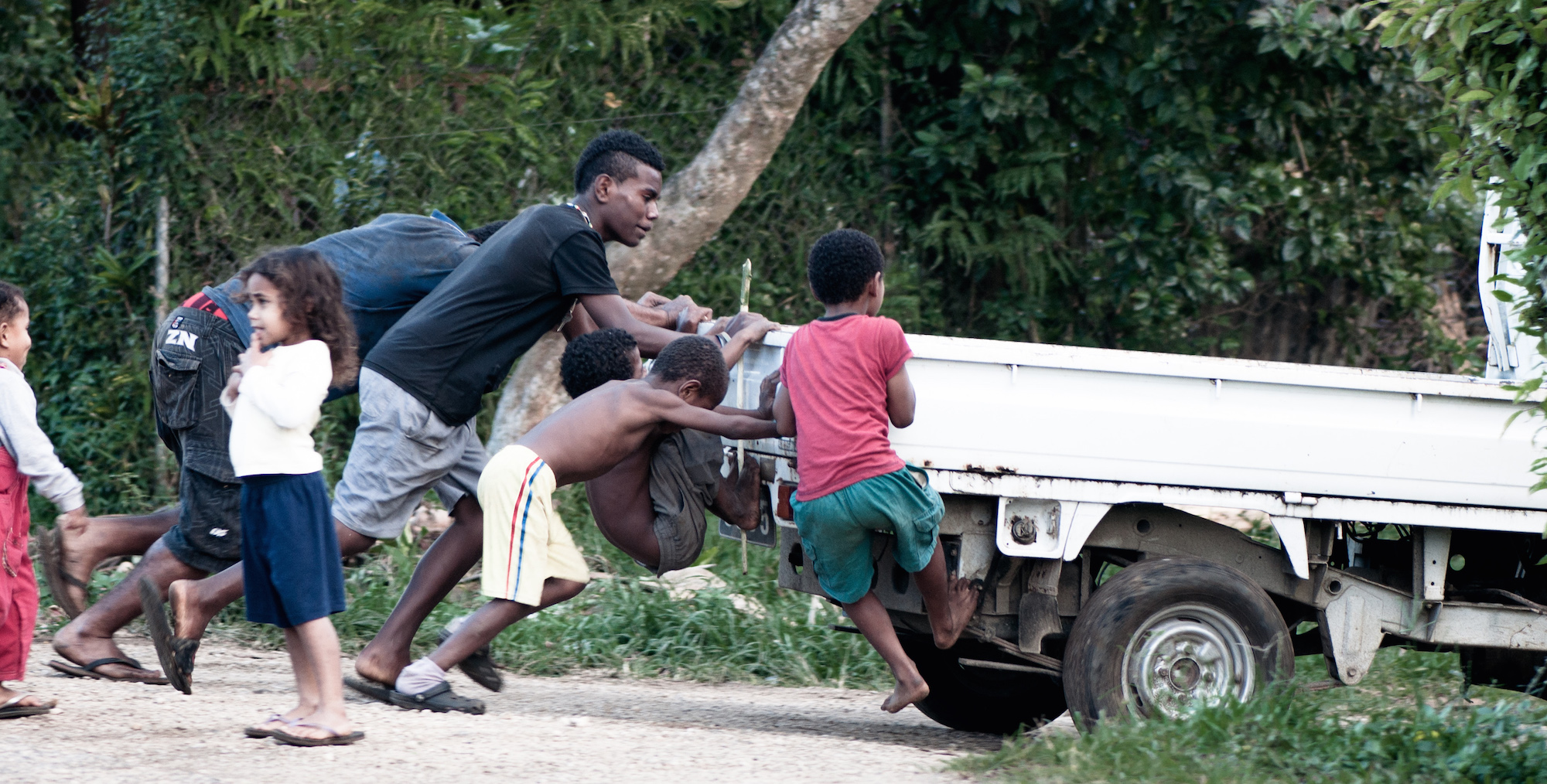
Make no mistake; that first step is a doozy. It’s allowed tens of thousands of people who never had any access at all to begin using the internet on a regular basis. As many a breathless commentator (including myself, on occasion) has noted, this has led to a vast increase in public dialogue online. This has led in turn to equally breathless speculation about the likelihood of a coming revolution in political awareness and activism, social justice, education and countless other shibboleths of progressive idealism.
With a few notable exceptions, commentators ignore key details about this incipient social revolution:
First, this ‘revolution’ resembles Iran’s Green movement more than Egypt’s uprising. In the vast majority of Pacific countries, price and availability limit access to all but a tiny proportion of the population. And these people are almost exclusively urban, affluent and educated. In short, they are already the best informed and most engaged. Simple arithmetic leads to the conclusion that limited access to internet limits the scope of its impact as well.
The internet is a ‘force multiplier’, in the sense that it renders many kinds of labour-intensive tasks vastly more efficient. While the impact on the minority who have recently begun to access it daily is immense, how much greater it could be if the other number in the equation (the sum of the population using it) were to rise even higher.
Second, the results of public dialogue, awareness and coordination on politics are measurable, but decidedly mixed. In Papua New Guinea, we saw a number of new faces in Parliament whose election can at least in part be attributed to the profile they garnered by participating in online fora such as Facebook’s Sharp Talk group. But we also saw many familiar faces returned, some of whom were widely reviled online. The same can be said of Vanuatu, where populist MP Ralph Regenvanu repeated his record-setting electoral performance, successfully expanded his base and managed to elect three other MPs under his Graon Mo Jastis (Land and Justice) banner. Regenvanu is the first politician since Independence to run an entirely issues-oriented campaign, and his appeal has only been amplified by his consistent presence online.
But popularity didn’t help Regenvanu on the tactical level. He won enough votes individually that, due to the vagaries of Vanuatu’s Single Non-Transferable Vote system (which elects multiple MPs in each constituency), he could have got three MPs past the post. Failures in messaging and on-the-ground organising, however, meant that his party’s second candidate in the capital constituency missed capturing the necessary votes to number him among the winners.
More to the point, Vanuatu too saw many familiar faces returned to Parliament. While its future seems uncertain, the current cabinet is nearly identical to the one that led the country to the polls only weeks ago. Even if it is ousted in the coming days, the champions and heroes of the small but growing online community can hope for a minority voice at best in any new government.
Third, and perhaps most importantly, commentators and researchers often underestimate the fragility of this flowering in the digital sphere and overstate its importance relative to other uses of digital communications. Despite the occasional public bun fight over self-censorship and media standards, it’s becoming increasingly clear that the Fiji government has been quite successful in its efforts to, in its words, ‘raise standards’ across the spectrum of media, both online and off, and to introduce ‘balance’. The stifling effects of official disapproval on certain kinds of commentary and content in Fiji are making themselves felt throughout the online community. They reach so far that it’s becoming harder to engage writers to perform any kind of independent analysis of government policy, ironically, even to praise it.
But to express unmitigated dismay at this outcome would be naïve, to say the least. Given that Fiji has the most highly developed telecommunications infrastructure in the region, and that the current regime has presided over its significant growth and improvement, why should we be surprised if they prove adept at making sure it serves their purposes? There is a very real chilling effect generated by the imposition of state views on the public dialogue, that’s true. But simply to write off the region-leading gains that have been made in telecommunications pricing and availability –as a recent Lowy paper did– is a textbook case of throwing the baby out with the bathwater.
In last week’s budget speech, Voreqe Bainimarama committed his government to building ten new telecentres in the coming year, and to removing duties entirely from smart phones in order to encourage uptake across the board. Informal reports indicate as well that there are plans afoot to provide broadband access to ‘almost 100%’ of the nation’s schools within the next four years.
The plain fact is that Fiji is a regional leader in understanding and embracing the importance of broad and deep investment in telecommunications capacity. They see their role in the coming years as that of a ‘knowledge hub’ for the Pacific.
Improved communications capacity, therefore, does not necessarily equate to increased freedom of speech, nor indeed the flowering of a diverse and broad-based social dialogue. This should not be news to us.
Melanesian and Polynesian societies all feature tight familial bonds and a preference for dialogue over confrontation. It’s not at all surprising, then, to see online groups arise whose membership comprises the majority of the online community. Hunger for change is generally evident, but it’s not overwhelming. There are in fact deeply conservative aspects to Pacific societies that can counterbalance and often quash an individual’s ability to enact change. Wantok-ism and a long tradition of respect for the so-called Big Man can overwhelm the desire to challenge the status quo.
If only to view the development of internet in the Pacific more clearly, it’s useful to look at online discourse and the networks that make it possible as separate, but linked endeavours. Building out infrastructure widely and deeply are necessary preconditions to achieving the progressive ends we most commonly associate with social media. But in and of themselves, they are not sufficient.
When we look at the landscape through this split prism, we can learn important lessons about how to achieve the former. The same paper that was so quick to toss aside Fiji’s recent gains ascribed the massive expansion of mobile services in the region to ‘deregulation’. Actually, the opposite is true. Virtually every successful step taken in this sector has been the result of increased government engagement in telecommunications: by negotiating (sometimes foisting) competition on incumbent monopolies, intervening when players tried to ignore or alter the rules, by closing the door to the back room and by giving their regulatory authorities the ability to bite back.
This may discomfit some, but in the Pacific it seems that more government, not less, is the recipe for success in terms of making the internet a part of their peoples’ lives. While Digicel’s example may have shown that even small markets can be profitable, the relatively large investments required to build out international fibre-optic links and robust nationwide networks carrying more than token bandwidth to the entire country are enough to make even the most risk-loving enterprise blanch. Simply put, no matter how much demand ensues, the capital investment costs per customer are astronomical.
It’s been argued that the only way a commercial entity can countenance such an investment is through a monopoly arrangement –the very thing that Pacific countries have spent the better part of a decade getting out from under. But even when other approaches are tried, the numbers are daunting. Tonga’s undersea cable connection to Fiji is heavily subsidised by the World Bank, and it’s being developed on a consortium basis, but the government the largest shareholder by a wide margin. Even with all of these interventions, prices promise to remain extremely high.
Simply put, it’s nearly impossible to make a profit-based business case for the kind of connectivity that will be required to provide affordable, widely accessible internet services in the Pacific. And those voice and data companies who do invest in the region will go to great lengths to protect their investment, up to and including interfering in the political process. The Pacific’s success (or failure) in embracing information technologies, therefore, will be determined by the level of commitment and firmness of will shown by government.
Even under the best possible circumstances, any gains will likely be tenuous. Renesys, the internet consulting group that broke the news of national internet blackouts in Iran, Egypt and more recently in Syria, recently used their international traffic monitoring tools to find out which countries were most vulnerable to disruptions in internet service. Needless to say, Pacific island countries were over-represented among those faced with ‘Severe’ or ‘Significant’ risk. Not even Fiji managed to find its way into the ‘Low’ risk category.
Renesys was worried mostly about the ease with which a government could turn off the internet tap on its own people. That may be a worry for some in the region, too, but those very same attributes that make national networks vulnerable to political interference also make them vulnerable to systemic threats. In 2004, the failure of a single satellite resulted in numerous nations going entirely dark, some for days. As the Renesys survey shows, little has changed in the interim.
If –and as we’ve seen, it’s a big if– Pacific nations do somehow succeed in integrating the internet into people’s daily lives, we still have no guarantee a flowering of awareness and online dialogue will necessarily follow. Once again, those in power will play an over-large role. No matter what decisions they make, there will be winners and losers at the top. Canny politicians and parties will follow the example set both by the insurgents in Vanuatu and PNG and by the incumbents in Fiji. Those who are adept at messaging and dialogue will likely flourish. Those who remain aloof, who ignore or refuse to take up these new social tools, will slowly (too slowly for some) but inevitably find themselves pushed to the sidelines. But they may succeed in slowing development for years before that happens.
The revolution, in other words, may not be digitised; there may not be any revolution at all. Every outcome, for better or for worse, will be determined by the will of governments to act.